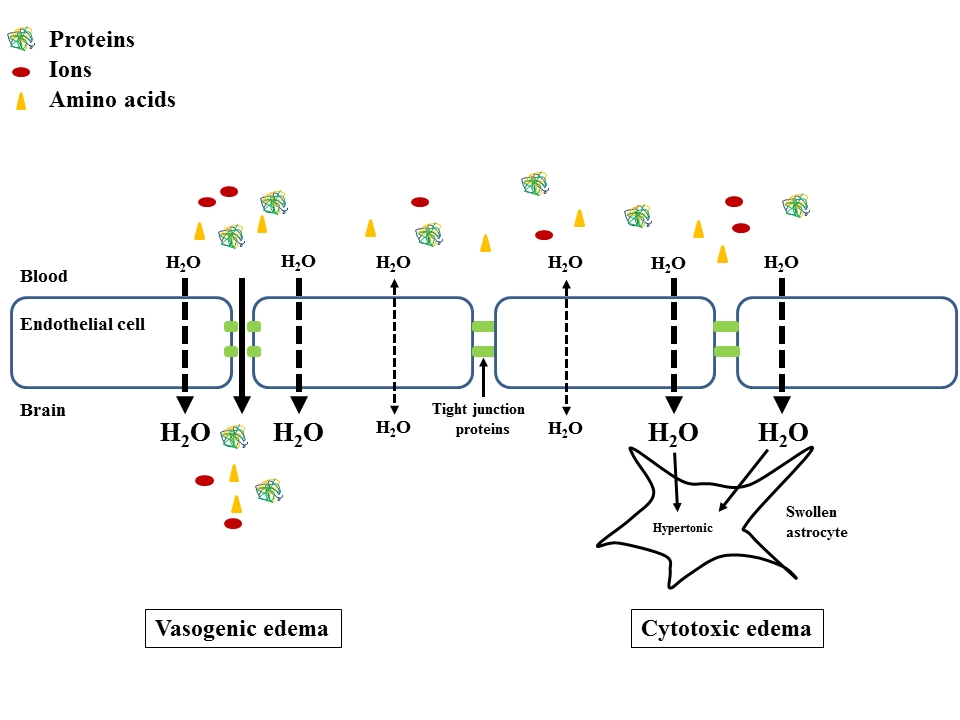
From Bosoi et al, Neurochem Int, 2013

Brain edema, an accumulation of water which leads to swelling of the brain, is commonly associated with HE. In acute liver failure, brain edema contributes to an increase in pressure in the skull which can be fatal. In cirrhosis, even though an increase in pressure within the skull is not observed, brain edema is still present. An accumulation of water in the brain is primarily due to swelling of the astrocytes (a type of brain cell). Astrocytes work very closely with neurons to help maintain normal brain function. However, swollen astrocytes lead to dysfunction in neurons and therefore brain function is impaired.
Learn more on cerebral edema and Bosoi et al, 2013.

From Bosoi et al, Neurochem Int, 2013